
Air pollution is an ongoing and growing crisis. Our air, indoor and outdoor, is full of hazardous emissions. Not only can this make us feel ill, but it can actually kill us.
In this article, we’ll cover air pollution facts that will scare you into making a change. Air pollution is causing global warming, millions of deaths every year, and putting our children’s lives at risk.
There are ways to protect yourself from air pollution, and we’ll cover those as well. But first, it’s time for the facts.
 Air Pollution Around The World
Air Pollution Around The World
Globally, 9 percent of all deaths are caused by air pollution (1). However, pollution levels vary throughout the world. See which countries are on either end of the spectrum.
- China is the largest emitter of carbon dioxide in the world. In 2017, they emitted 9.8 billion metric tons (2). This is mostly from coal burning, which releases huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the air we breathe.
- When China implemented a nationwide lockdown in early 2020 to control the spread of COVID-19, the Center for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) reported a significant decrease in CO2 emissions by at least 25% (3).
- After China, the U.S. is the most responsible for carbon dioxide emissions. In 2017, the U.S. emitted approximately 5.3 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide. This came from power generation, transport, and industry.
- When California’s stay-at-home order due to COVID-19 went into effect in March 2020, Los Angeles air quality improved by 20 percent and now has one of the cleanest air of any major city in the world, according to IQAir (4).
- India holds the title for being the world’s most polluted country when it comes to air quality. Out of the ten most polluted cities, seven of them are in India (5).
- New Dehli, India’s capital, is number 11 of the world’s most polluted cities, home to more than 20 million people. However, a week after the 2020 nationwide lockdown due to COVID-19, government data showed a 71 percent fall in particulate matter (PM 2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (6).
- On a bigger scale, Pakistan has the most polluted urban areas in the entire world, according to the WHO (7). Qatar and Afghanistan came in second and third.
- Air pollution is a worldwide crisis. According to this chart by Our World in Data, 16.5 percent of deaths in North Korea were caused by air pollution in 2017. In Nepal, 14.06 percent of deaths were caused by air pollution, and in India, 12.52 percent of deaths were caused by air pollution in 2017 (8).
- Deaths from air pollution are higher in South and East Asia than in the U.S., where 3.76 percent of deaths were caused by air pollution in 2017 (9).
- Up to 70 percent of air pollution is caused by road transport (10).
- On the other hand, let’s look at which countries are doing better when it comes to air pollution. Australia takes first place when it comes to low air pollution. The WHO ranked it as the least polluted country in the world (11).
- Brunei, compared to its nearby neighbors in Asia, is number two in the least air polluted countries in the world. It has made fiercely protecting its thick forests a priority.
- Not only is New Zealand a beautiful country, but it’s also number three in the least air polluted countries in the world. Every city in New Zealand matches the WHO’s recommendation of 10µg/m³.
 Air Pollution Affect Humans?
Air Pollution Affect Humans?
Breathing low quality air is more than a comfort issue. Air pollution is harmful to human health. It can cause temporary and permanent damage to our bodies.
- Air pollution is a silent killer that is globally responsible for 7 million premature deaths per year (12).
- Nine out of ten people breathe in polluted air, putting them at risk for health conditions such as stroke, heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, and acute respiratory infections.
- Air pollution is the cause of 16 percent of lung cancer deaths, 29 percent of heart disease and stroke, and 13 percent of deaths due to respiratory infection (13).
- Even if you don’t die from air pollution, it can still impact you, decreasing your quality of life. The tiny polluted elements in the air can get past our body’s defense system, entering our respiratory and circulatory system. This can damage your lungs, heart, and brain (14).
- Essentially, you’re breathing in poison that breaks down your lung’s protective barriers and causes inflammation. When this gets into your bloodstream, it can attack your whole body. This leads to increased blood pressure which can cause a stroke.
Asthma Attacks
- One of the most common symptoms of air pollution is a change in breathing. If you have asthma, you’re more at risk of air pollution.
- Research has found that children growing up in heavily polluted streets have smaller lung capacity than children living in cleaner areas. It impacts lung capacity by around five percent, and can’t be reversed (15).
- Air pollution can also be the cause of asthma. If you breathe in polluted air while pregnant, the chance that your child will develop asthma is increased (16). You’re still at risk of developing asthma from air pollution as an adult.
Allergies
- Allergies develop by disruptions in the immune system. Imagine what happens when you throw air pollution into the mix. Air polluters such as smoke enhance your body’s ability to produce IgE (the allergy antibody), increasing your chance of an allergic reaction (17).
- Another polluter, diesel exhaust, has been proven to enhance the ability to make IgE, also. Therefore, air pollution worsens allergies.
Lifespan
Even if you don’t develop one of the diseases listed above, you can still be affected by air pollution. What does this mean for our lifespan?
- Fossil fuel-driven air pollution has cut global life expectancy by 1.8 years (18).
- Air pollution has a worse effect on human lifespan than HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, smoking, and even war.
- If you live in one of the areas that exceed the WHO guidelines for particle pollution, you could be at risk of a decreased lifespan.
Our Daily Life
What about the effects air pollution has on our daily lives? This could affect your decision on which car to drive, where to live, and how to heat your home.
- If a member of your family has asthma or allergies, air pollution will be a big factor when it comes to deciding how you live your everyday life. Thanks to air pollution, there might be a big move to a safer country, such as New Zealand or Australia, in your future.
- Another element of everyday life you might want to sacrifice would be your car. Cars are one of the most common causes of air pollution. It’s safer for the environment to take the bus or the train, if possible, but the best way to travel is by foot or bike.
- The problem with this is that it can take up too much time. To get to work on time, you may need your car. Therefore, the habits we have in our everyday life actually end up contributing to the air pollution crisis.
 Air Pollution Affect The Environment?
Air Pollution Affect The Environment?
Human life is not the only biological component affected by air pollution. Poor indoor and outdoor air quality also harm our plants and animals.
- Air pollution affects humans as well as nature, plants, and animals.
- Things like aerosol cans, secondhand smoke, and wildfire are all air polluters that affect the environment (19)
- If you have visible air pollution that is hazy, that’s called smog. Smog affects shapes, colors, and the textures of the sights we see (20).
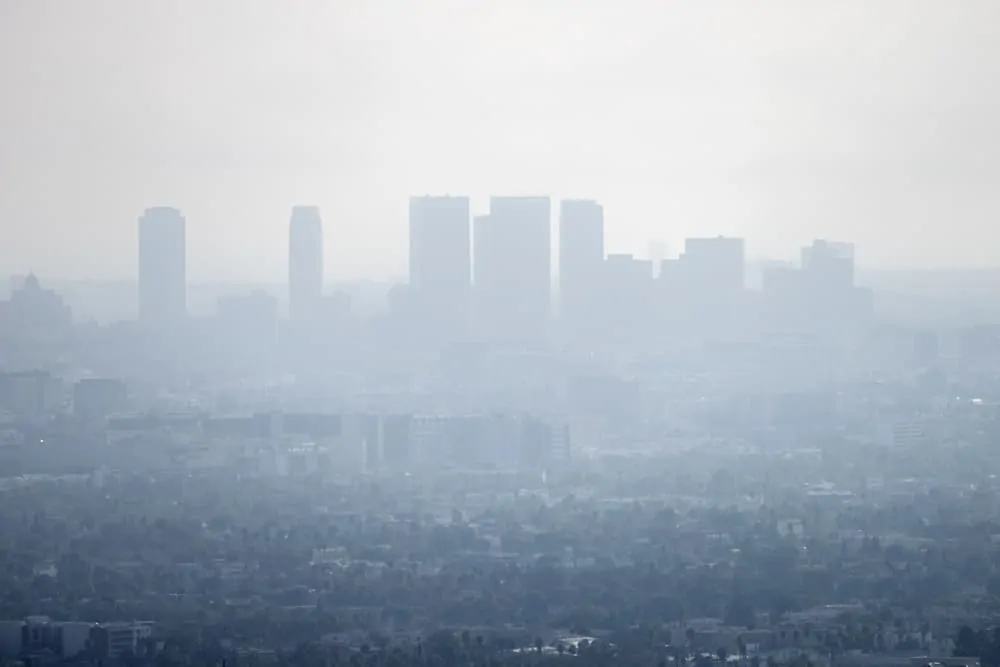

- One problem with air pollution is that it doesn’t stay in the air. Eventually, it falls back down to the ground. There, it contaminates waters, soil, crops, trees, and other plants (21).
- Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide particles in the air mix together with water and air to create acid rain. It’s harmful to nature because it changes the composition of and impacts the quality of plants, trees, and crops.
- Our poor animals are at risk, too. Studies show that air pollution contributes to birth defects, reproductive failure, and disease in animals (22). Because our oceans are polluted too, our aquatic life is also suffering the effects of air pollution.
- Ultimately, what this whole crisis is leading to is global warming, a hot topic right now. Literally. The temperature of our air and oceans are rising (23).
- The difficult problem is that we, as humans, have become reliant on these fossil fuels that are polluting the air. Cars, planes, heating homes, and running factories all burn fossil fuels.
 Indoor Air Pollution?
Indoor Air Pollution?
As humans, we spend most of our time indoors, whether we’re home, at work, out with friends, or at an event. It’s jarring to know that while we’re inside, we’re exposed to air pollution.
- The EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) has estimated that indoor air is nearly five times as polluted as outdoor air.
- The biggest sources of indoor air pollution include asbestos, formaldehyde, radon, tobacco smoke, mildew, mold, bacteria, wood stoves, fireplaces, and outdoor pollution making its way indoors (24).
- Indoor air pollution is so bad that it can potentially be up to 100 times worse than outdoor air pollution, in some rare cases (25). This isn’t in factories or building sites — this is in people’s homes.

- Secondhand smoke is one of the biggest indoor polluters in the world. You don’t have to be a smoker to experience the devastating effects of secondhand smoke.
- Since 70 of the 7,000 chemicals found in secondhand smoke can cause cancer, nobody is safe from secondhand smoke (26).
- Apart from lung cancer, indoor air pollution can cause pneumonia, stroke, heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (27).
 What Causes Air Pollution?
What Causes Air Pollution?
Air pollution is one of the biggest environmental problems we face in the world today. It occurs when hazardous particles and pollutants are released into the air (28).
Air pollution damages nature and the environment, but it’s also detrimental to our own health. Staying indoors doesn’t help either, because indoor air pollution exists, too (29). It’s terrifying to know that it’s all around us and there’s not much of an escape.
Air pollution is responsible for respiratory infections, heart disease, stroke, lung cancer, and death (30).
There are many sources of air pollution, including natural causes and human causes. Sources include gases, particulates, and biological molecules.
To break it down, here are some of the main polluters.
1. Particles From Burning Fuels
A common cause of air pollution is particles from burning fossil fuels (31). Carbon dioxide is produced as a result of burning these fuels. The pollution looks like soot, and it fills the air, making it hazardous to natural life.
Something you may do every day, such as driving your car, burns fuel and contributes to the air pollution crisis.
Carbon dioxide traps heat in the earth’s atmosphere, which is contributing to climate change (32).
2. Dangerous Gases From Chemicals And Secondhand Smoke
Gas from chemical and second-hand smoke is a common cause of air pollution. When these chemicals are in the atmosphere, they can cause acid rain and smog. These gases come from chemicals, soil, and smoke.
As well as the major causes such as factories and cars, these gases are also caused by secondhand smoke.
3. Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases have the devastating ability to trap earth’s heat in the atmosphere, which causes warmer temperatures, rising seas levels, extreme weather, and transmission of diseases such as Lyme (33).
Greenhouse gases are mostly made up of carbon dioxide, but another main greenhouse gas is methane. Methane comes from landfills, natural gas industry, and gas emitting from livestock.
 Prevent Air Pollution?
Prevent Air Pollution?
Thankfully, all hope is not lost. We still have a shot at beating or at least reducing air pollution — if we all play our part. Here’s what we can do.
- Using a True HEPA filter can remove 99.97% particle removal, limiting indoor air pollution (34).
- Air purifiers remove the source of your symptoms. If you struggle with headaches or asthma attacks from indoor air pollution, a purifier can help. This isn’t a replacement for medication, but it should limit your attacks.
- The Clean Air Act of 1970 aimed to regulate air emissions in the U.S. The law authorizes the EPA to establish National Ambient Air Quality Standards to protect the public and have more control over emissions of hazardous air pollutants (35).
- The Clean Air Act has reduced the ground-level ozone by more than 25 percent since 1980 (36).
- The Clean Air Act reduces the lead content in gas, cutting lead air pollution by 92 percent since 1980.
- Stop bad habits such as smoking. If you are indoors or around other people, specifically children, your secondhand smoke is extremely dangerous to them.
- When you are in traffic, turn off your engine, if possible. Sitting idly can make the air quality in your car up to 15 times worse than the air outside your car (37). Cars take in emissions from other cars around them and circulate that air within.
- If possible, invest in an electric car. Electric cars are cleaner for the environment than gas cars, by about 30 percent over the lifetime of the car (38).
- We can prevent further air pollution on a daily basis by walking or cycling to the places we need to go. Since car emissions are one of the biggest air polluters, treat your lungs and the environment with kindness by limiting the use of your car.
- If you can’t walk or cycle, take public transport. Taking the train or bus saves space on the road, gas, traffic noise, and emissions on the road. A 2004 study showed that taking public transportation saved 947 million gallons of fuel that would have been used if those passengers drove instead (39).
- Prevent indoor air pollution by ditching the non-organic cleaning products. A lot of store-bought cleaning products contain hazardous chemicals that pollute our indoor air (40).
- Ditch the candles, incense, perfumes, paints, glues, laundry detergent, and wood-burning fireplaces unless you know exactly what is in these products. They can all lead to indoor air pollution, making your home unsafe (41).
- Conserve energy. You can turn off lights when you aren’t using them to conserve energy and be greener. The more energy you waste, the more you pollute the air (42).
 Protect Yourself From Air Pollution
Protect Yourself From Air Pollution
Here are some tips to reduce your exposure to air pollution and its toxic side effects.
- Go green with public transport: As mentioned, it’s important to think green when it comes to public transport. Take the bus, train, or cycle.
- Move: If you’re in one of the most highly polluted areas, you could consider moving. This is a huge step, but it could add years to your life.
- Equip your kitchen: Make sure you have a hood over your stove to extract the chemicals from cooking out of your home.
- Watch out for certain building materials: If you live in a home with asbestos, formaldehyde, and lead, you are at risk of air pollution.
- Make your own: Although we said to ditch a lot of household cleaning supplies, you still need to replace them. You can easily make your own laundry detergent, surface cleaner, and fabric softener. Then you’ll know what ingredients you are using in the home, making the air cleaner.
- Check air quality: You can check the daily air quality with weather reports. If it’s a particularly bad day, avoid exercising or playing outdoors. Do an indoor activity such as mini-golf or seeing a movie.
- Don’t burn firewood or trash: It’s lovely to sit next to a cozy wood fire, but it’s not good for the environment. Protect yourself and your neighbors by recycling instead (43).
- Go bigger: Consider working with a charity or organization, such as Fighting for Healthy Air, to help the air pollution crisis.
 Air Pollution Is Serious
Air Pollution Is Serious
These facts are scary, as they show the real and deadly effects of the air pollution crisis. They highlight the pollutants emitted from our everyday habits such as driving, cleaning, and burning candles.
While fighting air pollution on a bigger scale depends upon our individual governments, you can make a difference in and around your home. Keep fighting for the cause, so that we can grow up in a healthy and safe world.
Artikel ini diambil dari ohsospotless.com dengan judul “50+ Shocking Facts About Air Pollution”, https://ohsospotless.com/air-pollution-facts/
Penulis/Editor : Beth McCallum
Foto Cover : Photo by veeterzy on Unsplash



